Direct-attached storage (DAS)
Direct-attached storage (DAS) is computer storage that is directly attached to one computer or server and is not, without special support, directly accessible to other ones. The main alternatives to direct-attached storage are network-attached storage (NAS) and the storage area network (SAN).
For an individual computer user, the hard drive is the usual form of direct-attached storage. In an enterprise, providing for storage that can be shared by multiple computers and their users tends to be more efficient and easier to manage.

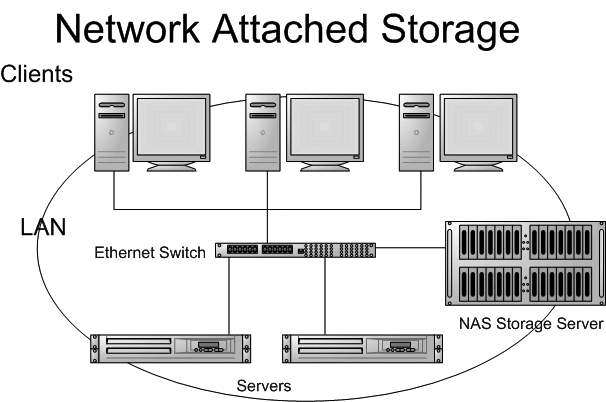
Network-attached storage (NAS) is hard disk storage that is set up with its own network address rather than being attached to the department computer that is serving applications to a network's workstation users. By removing storage access and its management from the department server, both application programming and files can be served faster because they are not competing for the same processor resources. The network-attached storage device is attached to a local area network (typically, an Ethernet network) and assigned anIP address
File requests are mapped by the main server to the NAS file server.
Network-attached storage consists of hard disk storage, including multi-disk RAID systems, and software for configuring and mapping file locations to the network-attached device. Network-attached storage can be a step toward and included as part of a more sophisticated storage system known as a storage area network (SAN).
NAS software can usually handle a number of network protocols, including Microsoft'sInternetwork Packet Exchange and NetBEUI, Novell's Netware Internetwork Packet Exchange, and Sun Microsystems' Network File System. Configuration, including the setting of user access priorities, is usually possible using a Web browser.
Storage area network (SAN)
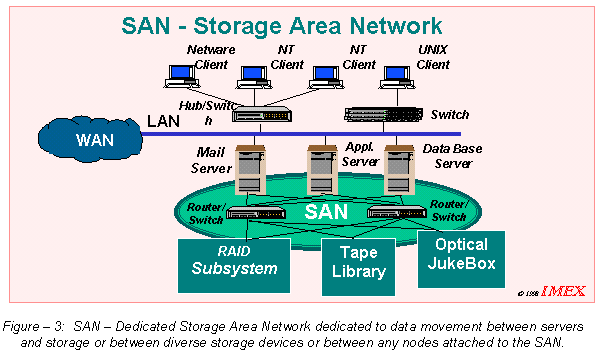
A storage area network (SAN) is a high-speed special-purpose network (or subnetwork) that interconnects different kinds of data storage devices with associated data servers on behalf of a larger network of users.
Typically, a storage area network is part of the overall network of computing resources for an enterprise. A storage area network is usually clustered in close proximity to other computing resources such as IBM z990
mainframes but may also extend to remote locations forbackup and archival storage, using wide area network carrier technologies such as ATM or SONET.
A storage area network can use existing communication technology such as IBM's optical fiber ESCON or use Fibre Channel technology. Some SAN system integrators liken it to the common storage bus (flow of data) in a personal computer that is shared by different kinds of storage devices such as a hard disk or a CD-ROM player.
SANs support disk mirroring, backup and restore, archival and retrieval of archived data, data migration from one storage device to another and the sharing of data among different servers in a network. SANs can incorporate subnetworks with network-attached storage (NAS) systems.
No comments:
Post a Comment